Are you planning a trip to any beach or the mountains with your baby? Or stepping out in the Sun with the kid in the toe? Don’t forget the baby sunscreen.
Read on to know the benefits of sunscreen for your baby. And understand what features to look for when choosing a sunscreen suitable for your child.
Why use a baby sunscreen
Is baby sunscreen is useful? Well yes; but first let’s understand why skin experts recommend sunscreen in first place.
Protection from UV radiation
Sun rays contain UV radiations. Although sunlight has various health benefits [1], they are a known carcinogen. There are 3 types of UV radiations [2]:

source: https://goo.gl/Envhtq
- UVA – penetrate the atmosphere, can cause skin ageing, wrinkles & few types of skin cancers
- UVB – penetrate the atmosphere, more potent than UVA, can cause skin burn & various types of skin cancers
- UVC – do not penetrate the atmosphere, not known for causing cancer
Both UVA and UVB are known to harm the skin and cause skin cancer. The intensity and effect of these radiations vary based on the latitude, altitude, season, time of the day, etc..
While UVB is more potent than UVA, protection from both the rays is required.
The strength of these rays determines the amount of exposure to the radiation. But, limiting the duration of direct exposure to sunlight, and following a protective regime can reduce the extent of this exposure. Click here to read more about how to protect kids from harmful UV radiations.
A sunscreen is universally accepted as a beneficial part of a sun protection regime.
Decoding the sunscreen features
Indian skin type is prone to more tanning (due to UVA) and lesser sunburning (due to UVB) [3]. Sunscreen is effective if it protects from both UVA & UVB. The extent of protection from these rays is indicated via different labelling/rating system. The most common ones are:
- SPF value indicating protection from UVB
- Broad spectrum/PA rating indicating protection from UVA
1. SPF value – UVB protection
Sun protection factor (SPF) value is a number to measure the fraction of sunburn-producing UV rays that reach the skin. For example, “SPF 30” means that 1⁄30 of the burning radiation reaches the skin surface through the recommended thickness of sunscreen. So, if a person gets a sunburn without using sunscreen after 20 minutes of exposure to sunlight, applying a recommended amount/thickness of sunscreen with SPF 30 would prolong the time for same degree of sunburn to around 600 (20×30) minutes. UVB causes sunburn, and SPF value indicates the degree of protection from UVB.
Note: A higher SPF does not necessarily mean proportionally higher protection. Between SPF 15 to SPF 50, the protection increases from 93% to 97% screening of sunrays.
Usually, the SPF value of 15-30 is recommended in India.
2. Broad spectrum/PA rating – UVA protection
Different brands have different ways of labelling protection from UV radiation. There is no universal indicator of labelling or indicating protection from both UVA and UVB radiation. Also, SPF value does not indicate protection from UVA & UVB.

source: https://goo.gl/Envhtq
Many sunscreens offer protection from UVB only. This partly due to the older belief that only UVB is harmful. But many studies and research conclusively show that protection from both UVA and UVB is required. Different countries across the globe have different standard/regulation for indicating protection from UVA & UVB radiation. US FDA mandates a “broad spectrum” labelling indicating UVA protection proportional to the UVB protection, using a standardised testing method. While Europe adopts a star rating system, many Asian nations have a PA rating system [4].
In India, there is no specific regulation for labelling of UVA protection (or UV protection in general). But a general guideline is to look for “broad spectrum” label, PA rating, or clear label indicating protection from both UVA & UVB.
A “Broad spectrum” label or a PA++ or PA+++ rating is considered good protection from UVA.
Types of sunscreens
To understand what is the right sunscreen for your child, let,s look at the two types of sunscreens available, based on the mode of protecting:
- Physical sunscreen: forms a reflective layer on top of the skin; contains ingredients to reflect the sunlight and prevents sunlight from reaching the skin
- Chemical sunscreen: forms an absorbing layer on top of the skin; contains ingredients to absorbs the UV radiation from the Sun and prevent it from reaching the skin cells
So a sunblock or sun lotion or sunscreen may differ in its mode of action of UV protection. It may contain ingredients for the chemical or physical screening of the sunlight or a combination of both.
A sunblock is many times a physical sunscreen though not necessarily. As already mentioned the sunblock vs sunscreen vs sun lotion is very interchangeably used.
Physical sunscreen:
Physical sunscreen is usually oil based and forms a thick water-resistant reflective layer on the skin. It usually contains naturally occurring minerals as active ingredients. Some people consider it safer for the skin. However, it may appear dense white on the skin. Will your toddler find it too amusing to rub/lick it off?
Chemical sunscreen:
A chemical sunscreen, on the other hand, uses sunlight absorbing chemicals to form an absorbing layer on the skin. So, some people fear it can irritate sensitive skin. It usually forms a thinner layer, absorbs well and has an aesthetically better appearance than physical sunscreen.
Both are effective in protection from UV radiation when correctly used [5].
Baby sunscreen
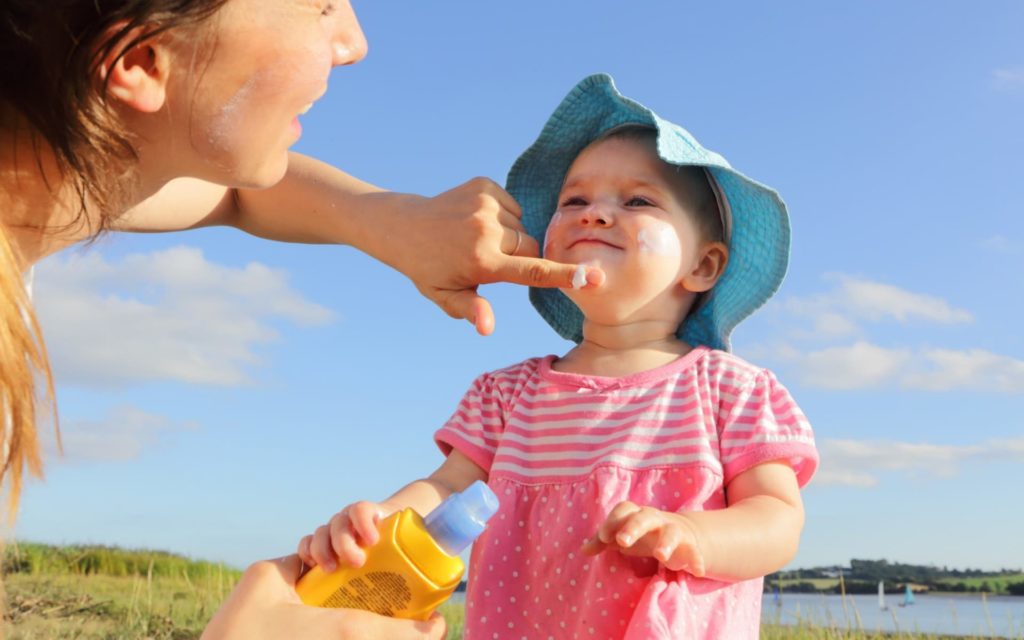

source: https://goo.gl/8QdNBv
Sunscreen helps to prevent sunburn, premature ageing or skin cancer caused due to exposure to UV radiation. Is there a special formulation for baby sunscreen? Most of the paediatricians in India would recommend any regular sunscreen with the following features:
-
Protection from UVB: SPF value of 15 (everyday use) or 30 (extended exposure)
-
Protection from UVA: ‘Broad spectrum’ label or PA++/PA+++ rating
-
Protecting kids from UV rays in water: Water resistant sunscreen
Any baby sunscreen should have these features. A baby sunscreen may be specially formulated for a child’s sensitive skin. But if you patch test a regular sunscreen on your child’s skin, and he is fine, even a regular sunscreen works for a baby as well.
Click here for recommendations on buying a suitable sunscreen for your baby.
Note: No sunscreen remains effective beyond 2-3 hours. Hence you need to reapply as recommended by the manufacturer for continued protection when you are outdoors in the Sun.
Should you use sunscreen for the baby
Many parents worry about the use of chemicals on their baby’s sensitive skin. With commercial, large-scale production of baby products, the chances of harmful additives, carcinogens, or skin irritants are not so uncommon in baby products.
While universally sunscreen is recommended as an effective way to protect from UV radiation, commercially produced sunscreens have their fair share of controversies. Mainly:
- Adverse effects of chemicals on the skin: The presence of nanoparticles in the sunscreen can potentially have adverse effects on the skin
- Vitamin D deficiency: application of sunscreen hampers synthesis of Vitamin D
- Adverse impacts of chemicals on marine/ocean life: chemicals in sunscreen can have a toxic effect on the corals and other marine beings
However, you can opt for a sunscreen that is safe for the environment and your child. Or a sun protection regime which uses sunscreen (not in amount) only when exposure to sunlight is unavoidable.
Conclusion
Experts recommend applying sunscreen, to 6+ months old babies, when exposed to the Sun, especially during intense heat hours. While buying a baby sunscreen one must look at these essential features:
- SPF value 15 or 30
- ‘Broad spectrum’ label or PA++/PA+++ rating
- Water resistant sunscreen when going in water
Sunscreen may be a physical sunscreen (reflects UV radiation) or a chemical sunscreen (absorbs UV radiation) or a combination of both. Both are effective as long as they protect from both UVA & UVB.
Choose a sunscreen which is safe for your baby’s sensitive skin.





Leave A Comment